Rotary heat exchangers
85%
Efficiency
85%
Efficiency
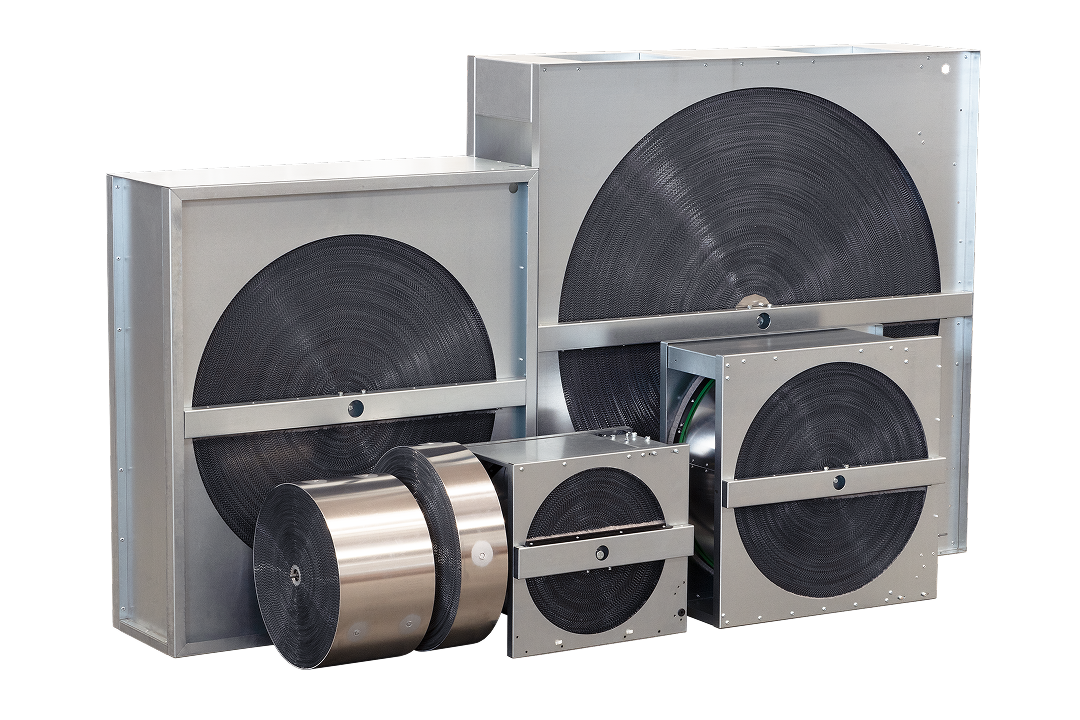

Product categories
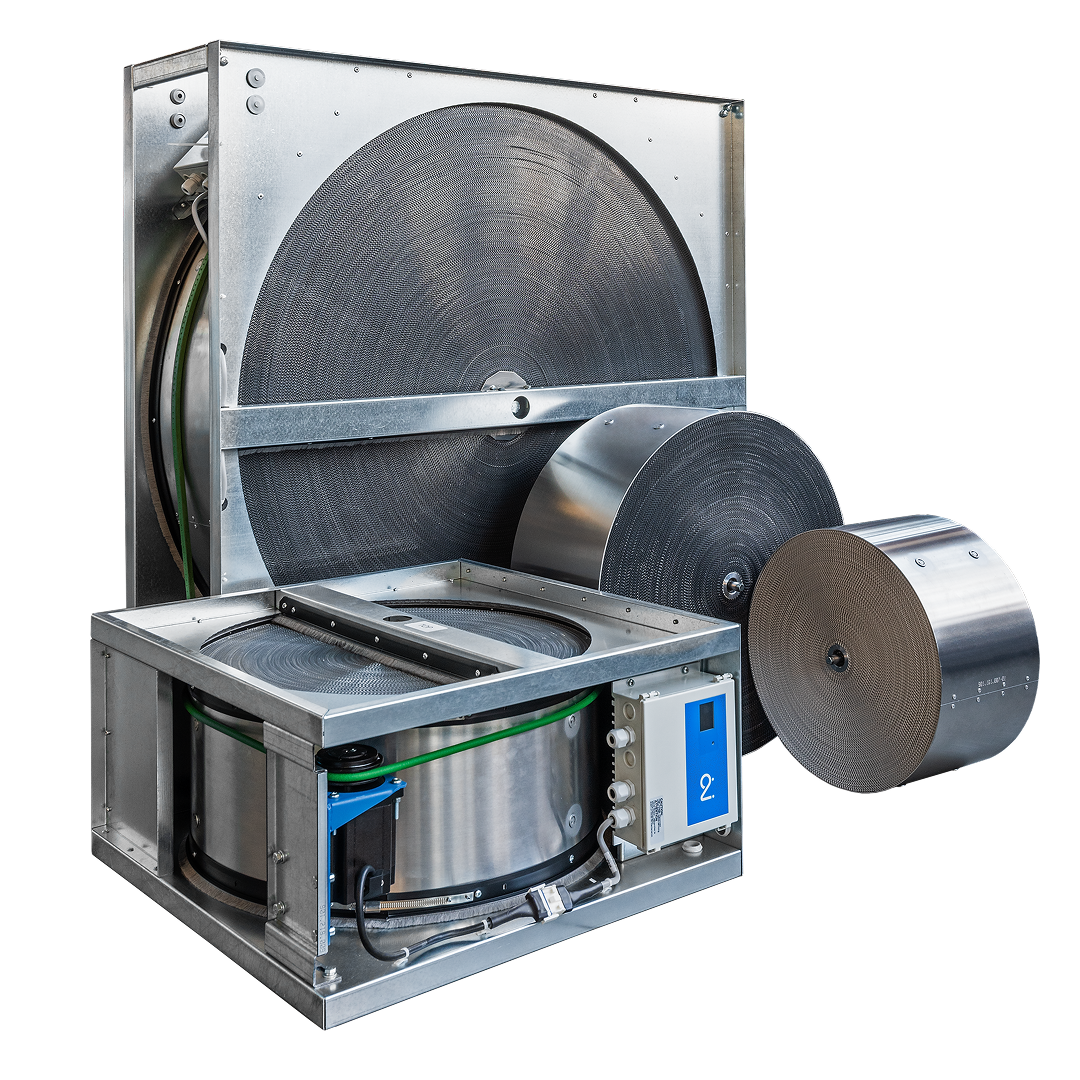

Condensing rotary heat exchangers
Series:
R-EX
Sensible-only heat recovery for dry ventilation where humidity transfer is not required. It is efficient and easy to integrate.
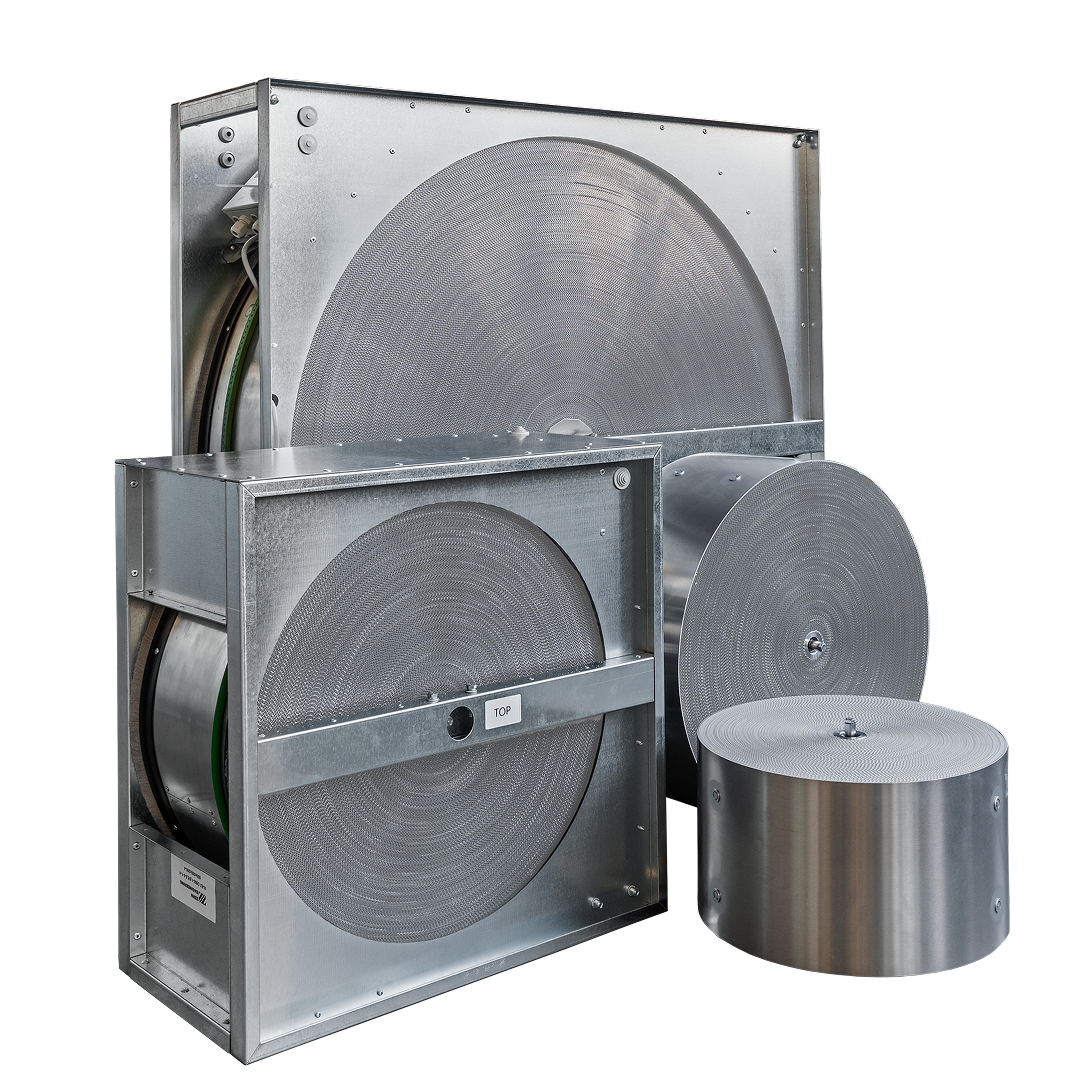

Enthalpy rotary heat exchanger
Series:
R-E-EX
Hygroscopic coating transfers heat and moisture to help keep indoor RH comfortable in homes, offices, and public spaces.
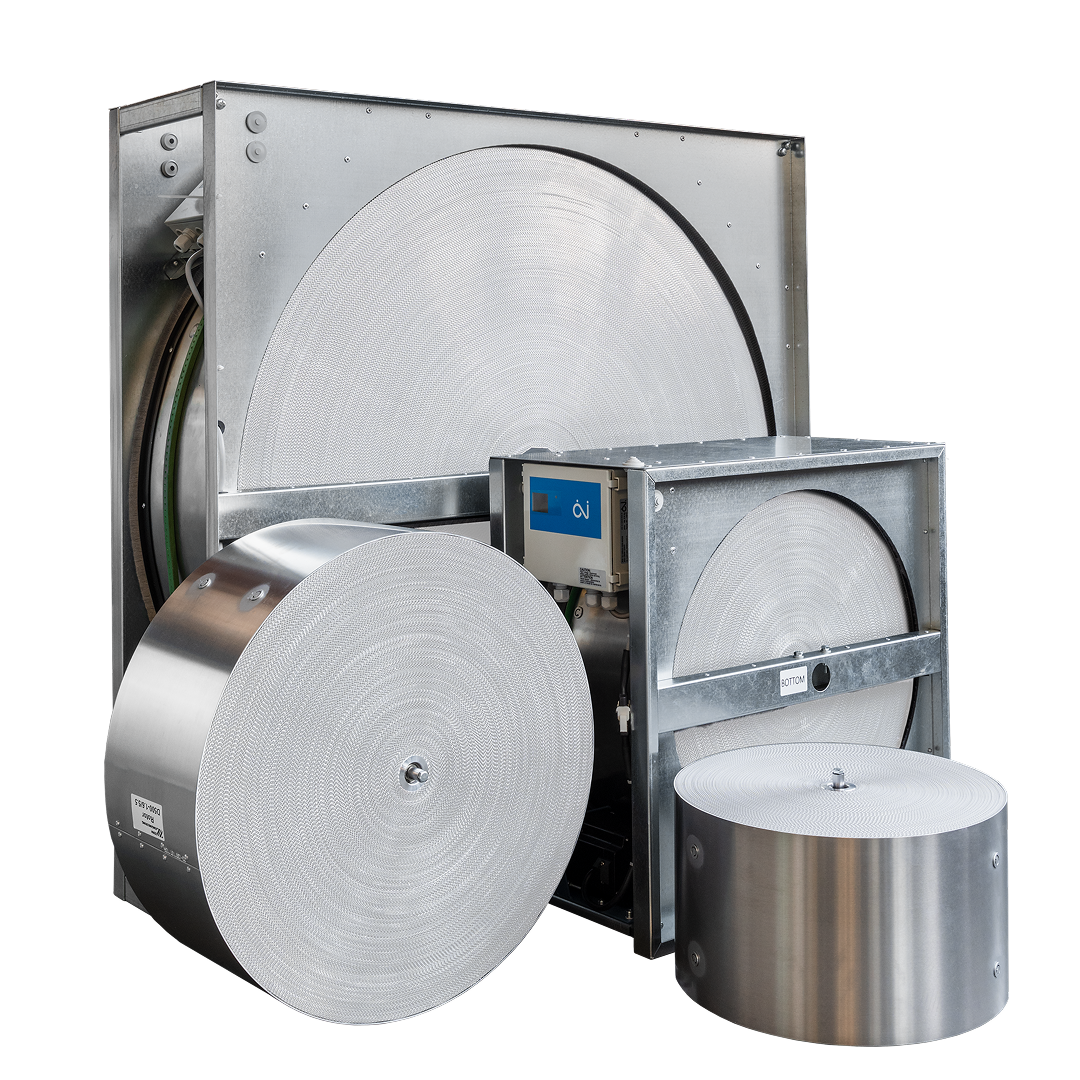

Sorption rotary heat exchanger
Series:
R-N-EX
Advanced sorptive layer for high moisture recovery and stable indoor climate — well suited for swimming pools, fitness centers, and demanding commercial spaces.
Technical features
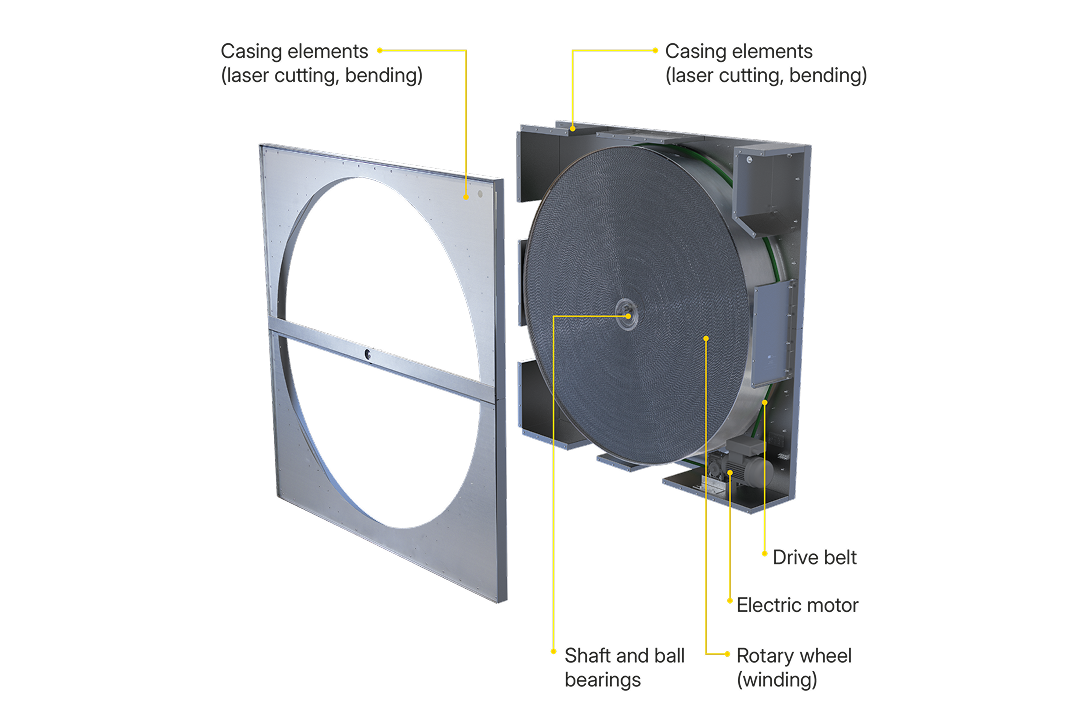
A rotary heat exchanger consists of a rotating wheel made up of numerous small air ducts or channels, typically constructed from aluminum. This wheel rotates between two separate air streams: the warm exhaust air and the cooler incoming fresh air. As the wheel turns, it absorbs heat from the outgoing air and transfers it to the incoming air, effectively recovering energy that would otherwise be lost. In units equipped with hygroscopic coatings, moisture can also be transferred, facilitating humidity control.
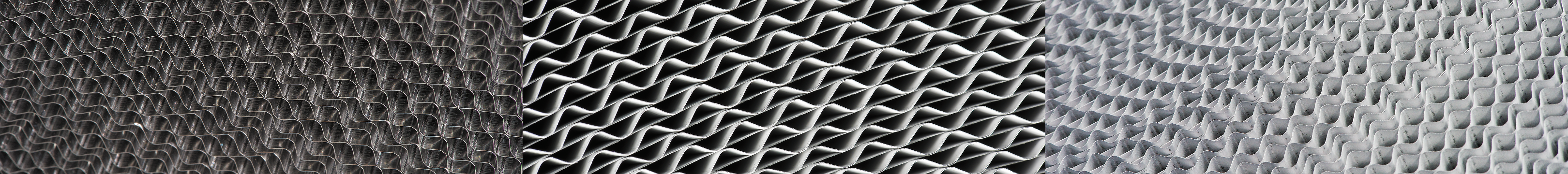
Modifications
Rotor (matrix)

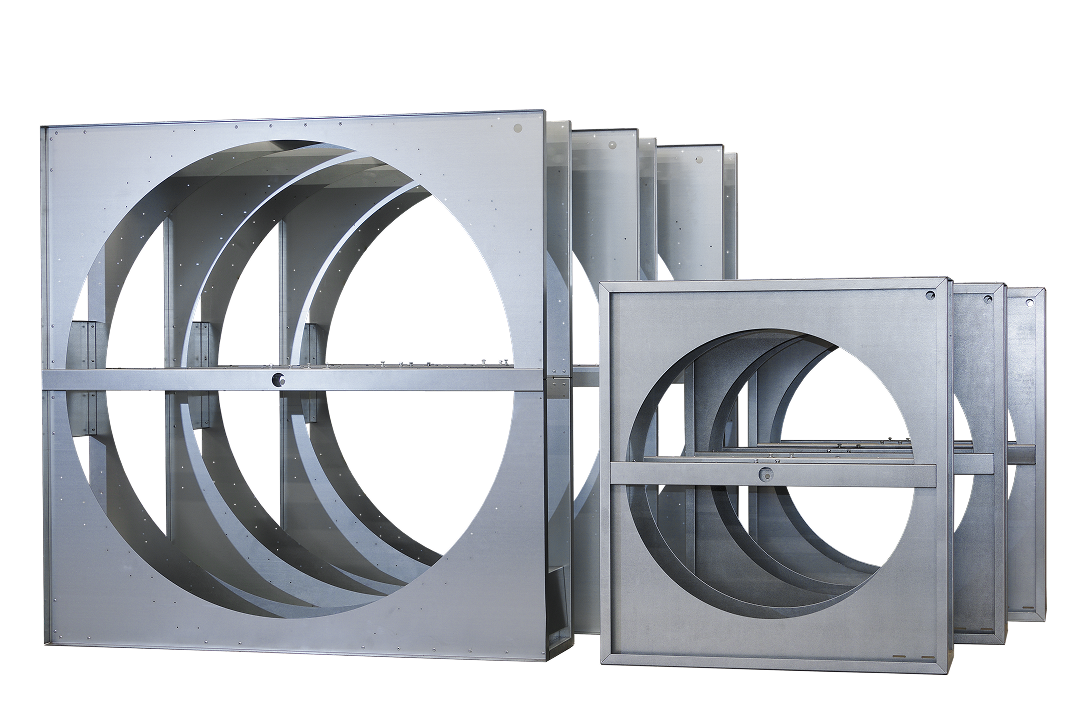
Casing
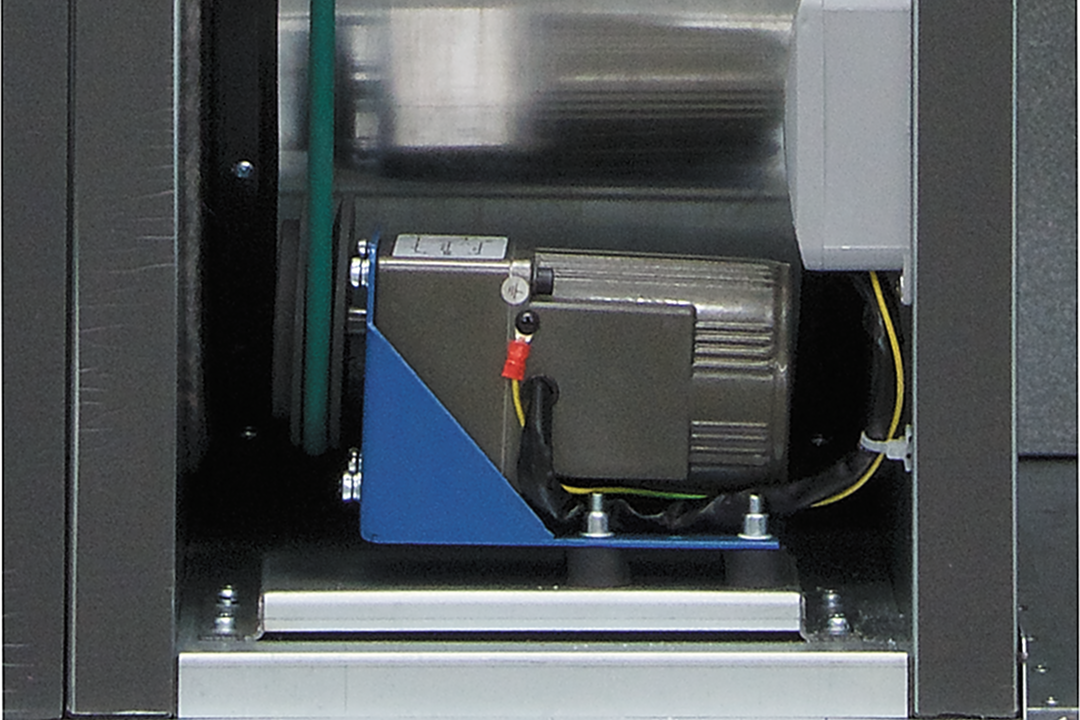
Drive
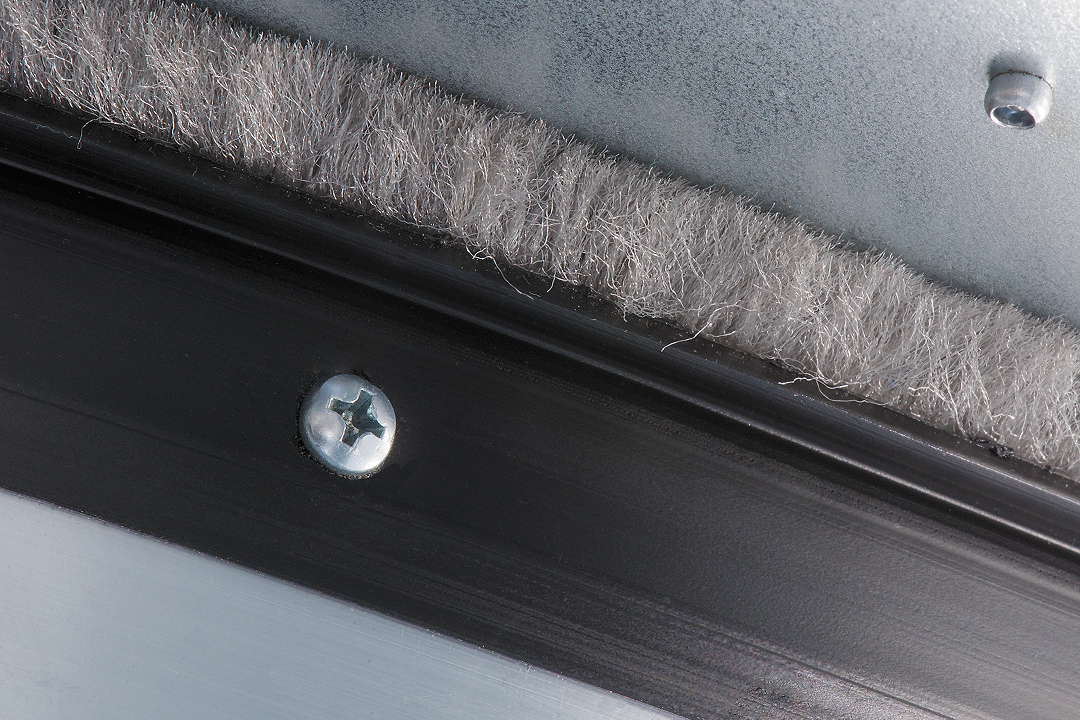
Sealing system
High-quality seals minimize leakage and cross-contamination.
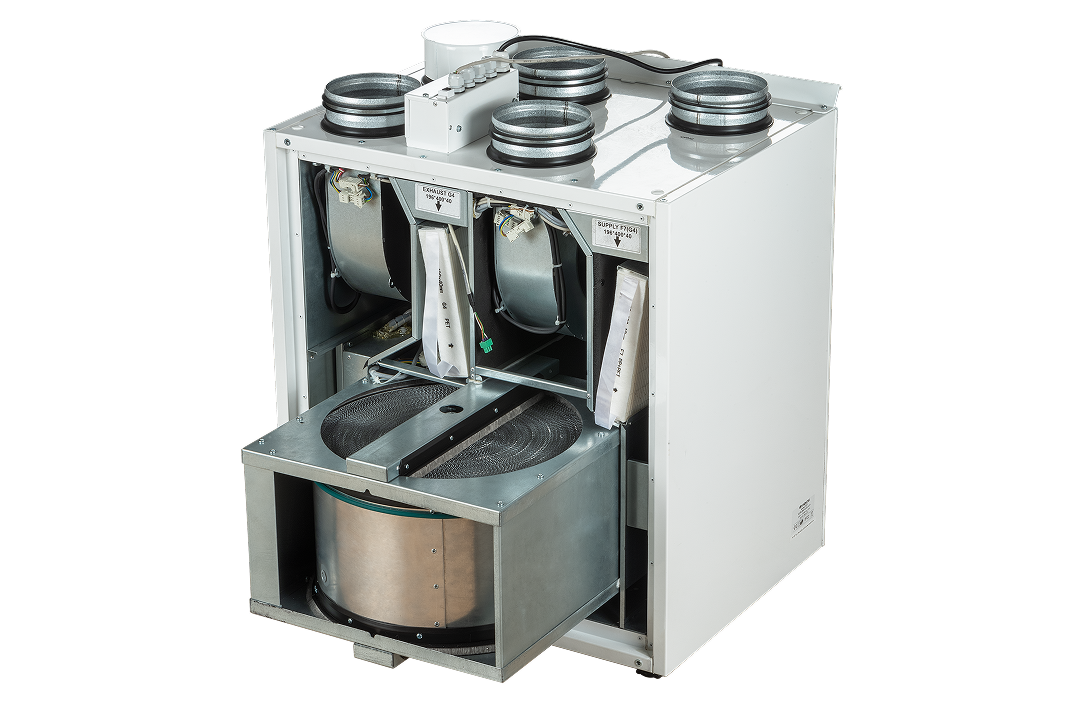


Product catalog
Discover ZERN ENGINEERING’s full range of heat exchangers. Our product catalog provides detailed specifications, material options, and performance data to help you select the optimal solution for any application